GOAT BitVM2 Testnet User Guide
Introduction
GOAT BitVM2 Testnet was born to enable efficient interoperability between the Bitcoin and the GOAT Network.
🚀 Enjoy GOAT BitVM2 Testnet V3
👉 https://bitvm2-testnet4.goat.network (opens in a new tab)
BitVM2 is a permissionless bridge protocol that enables Bitcoin to verify arbitrary off-chain computations without a hard fork, using presigned transactions, one-time signatures, and SNARK proofs. It improves capital efficiency over BitVM by allowing anyone to challenge and penalize a faulty operator within three on-chain transactions and a delay of no more than 2–3 weeks, though it remains impractical for real-world deployment.
GOAT BitVM2 extends BitVM2 into a standard Bitcoin zkRollup by solving key limitations such as operator double-spending, inefficient reimbursement, and lack of incentives mechanism. GOAT BitVM2 can allow any operator to finish the reimbursement in 1 day with the power of zkMIPS and multi-round randomized challenge mechanism, and prevent the operator's double spend issues by verifying the Rollup chain's consensus lightclient.
Combined with GOAT Network's decentralized sequencer and zkMIPS, GOAT BitVM2 enables GOAT Network to be the first native Bitcoin zkRollup with real yield. See more at GOAT BitVM2 White Paper (opens in a new tab).
BitVM2 Bridge Guide
BitVM2 Bridge is a practical application of the BitVM2 protocol that makes it possible to earn native Bitcoin yield. This feature is open to anyone.
Bridge In
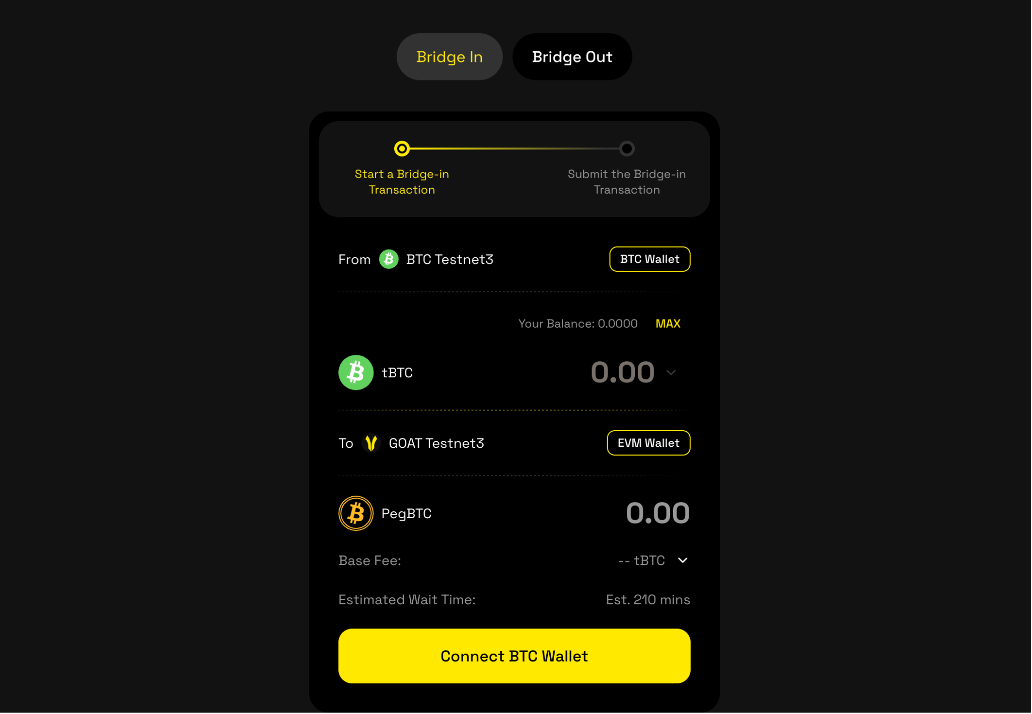
- In Step 1, connect your BTC wallet and EVM wallet first.
- Choose the amount you want to bridge in.
- Select the fee rate for the Bitcoin network — this affects the processing speed of your transaction. Click [Next] to proceed to Step 2.
- In Step 2, wait for all committee members to verify the transaction. Click [Refresh] to update the progress.
- Once this transaction is ready to submit, click [Submit].
- Confirm the transaction in your wallet and pay the base fee.
- After successful submission, the funds will arrive in approximately 60 minutes. Please wait patiently. Track the transaction status in 'History'. Note: Arrival time may vary depending on Bitcoin network congestion.
- Once the transaction is confirmed, the funds will appear in your receiving wallet.
Bridge Out
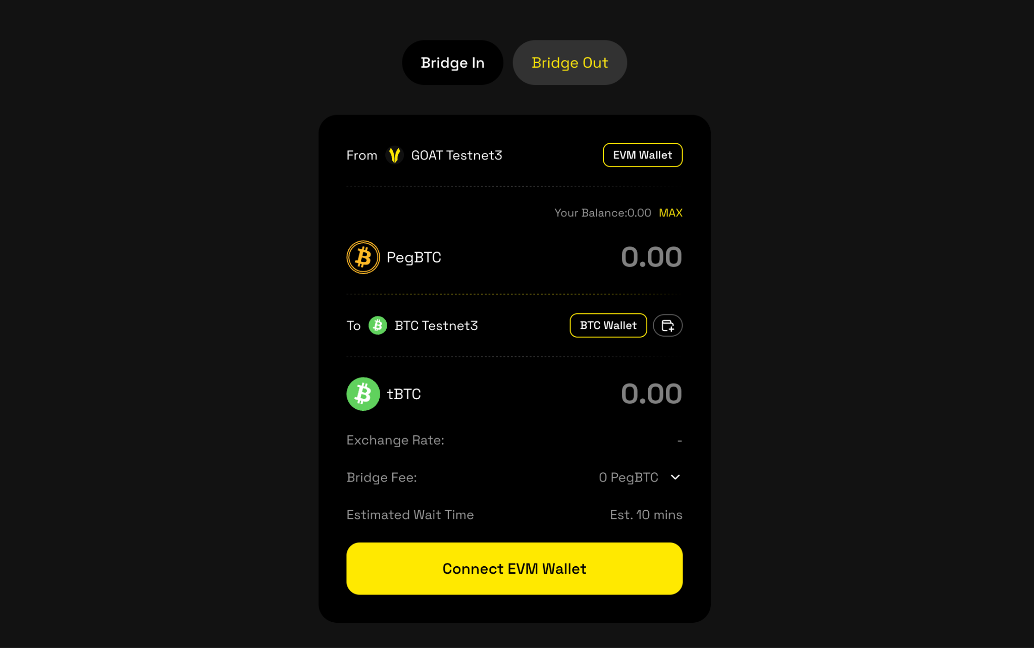
- Connect your EVM wallet and BTC wallet first.
- Enter the amount you want to bridge, making sure it meets the minimum required amount.
- Double-check the cross-chain information: amount, exchange rate and bridge fee.
- Submit this transaction within the valid period, please click [Submit].
- Confirm the transaction in your wallet and pay the gas fee.
- After successful submission, the funds will arrive in approximately 60 minutes. Please wait patiently. Track the transaction status in 'History'. Note: Arrival time may vary depending on Bitcoin network congestion.
- Once the transaction is confirmed, the funds will appear in your receiving wallet.
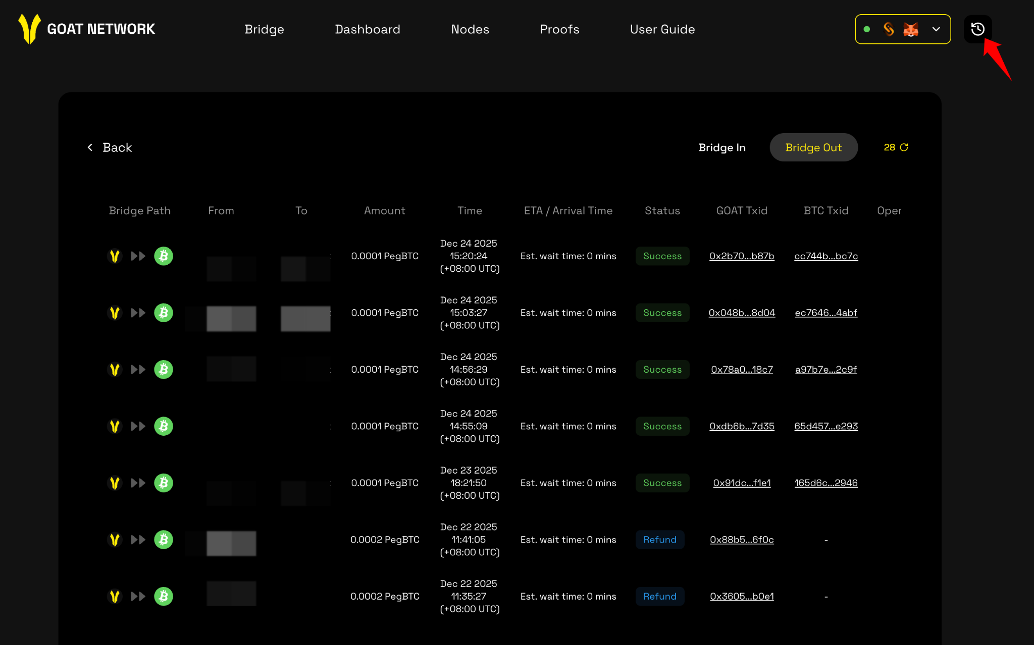
History
After completing any bridge-in or bridge-out transaction, you can find it in 'History'. You can also track the transaction progress in real-time here and monitor the arrival status.
BitVM2 Peg-out Guide
As a key component of the GOAT BitVM2 protocol, operators obtain native BTC through redeeming PegBTC. Only operators participating in Peg-in can use this feature to peg out a specific amount of BTC.
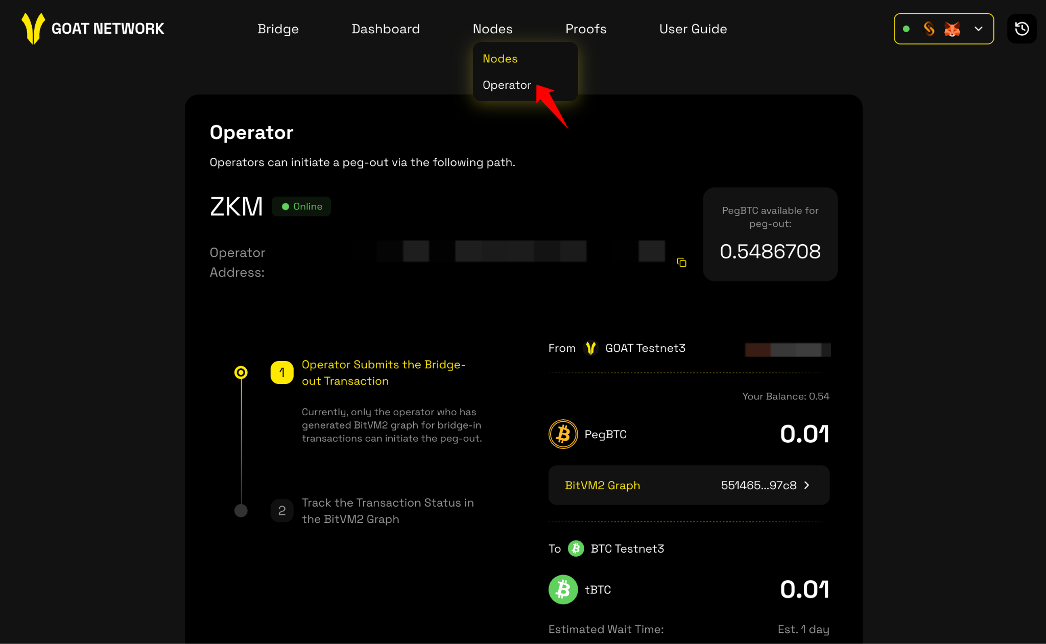
- Simply connect your EVM wallet.
- The system will default to showing the instances you can peg-out. You can see the amount available for this peg-out.
- Click [Approve] — your wallet will prompt an approval window. Please approve the maximum amount you intend to transact.
- After the approval is successful, return to the interface and click [Submit]. Your wallet will prompt a transaction confirmation window. Confirm the transaction and pay the gas fee.
- In Step 2, this indicates you have successfully kicked off the process. You can click [BitVM2 Graph] to track the bridge-out progress.
- You can also track the transaction status and results in peg-out history.
- Once the peg-out is successful, the funds will appear in your receiving wallet.
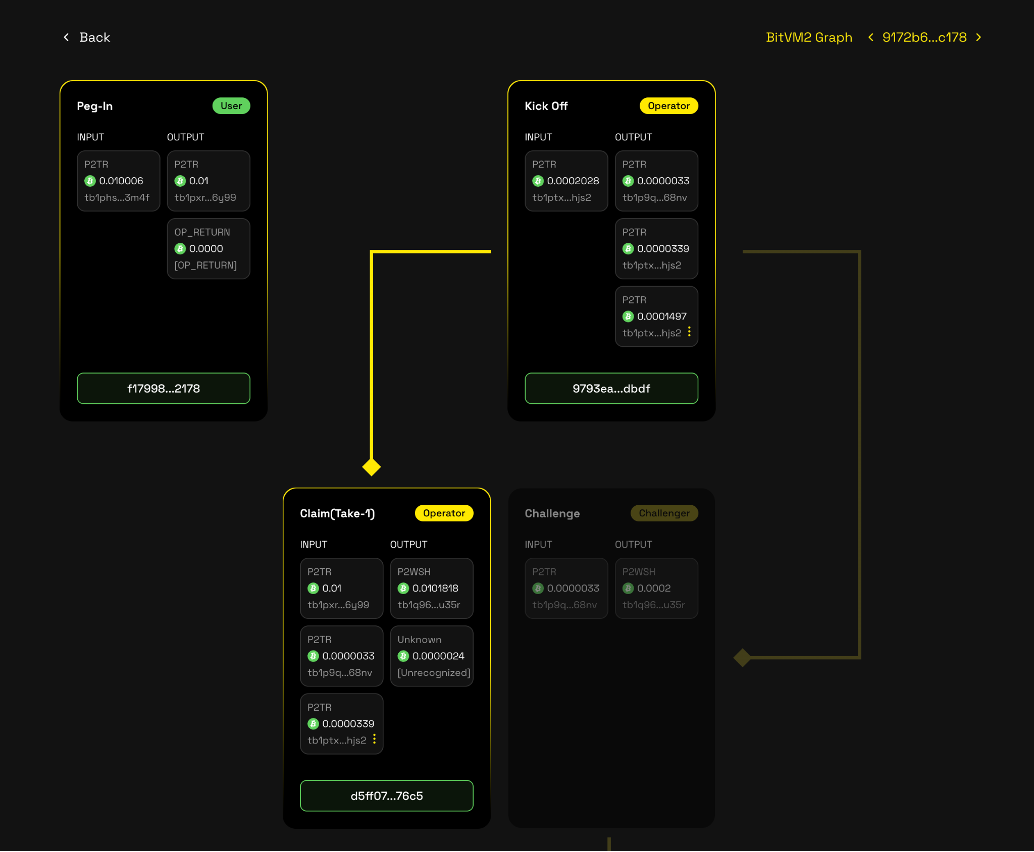
BitVM2 Graph
The BitVM2 Graph provides a clear visual representation of how the GOAT BitVM2 protocol operates. It clearly illustrates the workflow and interactions between different stages. Please review the following case study to gain a comprehensive understanding of the protocol's mechanics.
Case 1: Initial State (Only Peg-in Active)
- Status: Pending Peg-out / Active Deposits
- Description: Currently, only Peg-in transactions have been processed, and the BTC remains locked in the vault. No Operator has initiated a Peg-out request yet. The system is in a stable state, awaiting withdrawal triggers from Layer 2.
Case 2: Standard Path (Successful Reimbursement via Take-1)
- Status: Withdrawal Completed (Fast Track)
- Description: The Operator successfully initiated the Peg-out and broadcasted the Kickoff transaction. Since no challenges were raised during the T1 time-lock window, the Operator proceeded to the Take-1 stage. The Operator has been reimbursed, and the corresponding pegBTC has been burned in the Layer 2 contract.
Case 3: Challenge Successful (Operator Misconduct Slashed)
- Status: Withdrawal Intercepted (Disprove Stage)
- Description: A Challenger detected Operator misconduct and successfully initiated a dispute. The Operator failed to provide valid Watchtower Proofs or submitted an invalid Assert. Consequently, the challenge was upheld, the Operator's collateral was slashed, and the reimbursement was denied. The Challenger/Relayer received compensation for the protocol's security maintenance.
Case 4: Challenge Failed (Successful Reimbursement via Take-2)
- Status: Withdrawal Finalized (Dispute Resolved)
- Description: A challenge was raised, but the Operator successfully defended the withdrawal by providing all required Watchtower Proofs and valid Assert transactions. After the T5 and T6 time-locks expired, the challenge was deemed invalid. The Operator successfully received reimbursement via the Take-2 stage, proving the legitimacy of the Peg-out.
Join GOAT BitVM2 Testnet
Node Requirements (Testnet)
1. Watchtower
- After being endorsed by the committee multisig (multisig tooling not yet implemented), the watchtower writes data on-chain.
- The L1 address must maintain sufficient balance to pay watchtower challenge fees.
- Each challenge costs approximately 4,000 sats.
2. Challenger: Permissionless
- The L1 address must maintain sufficient balance to cover:
- Challenge transaction fees
- Challenge bond
- For each challenge:
- Bond: 20,000 sats
- Transaction fee: ~1,000 sats
3. Operator: Permissionless.
Layer 1 (Bitcoin)
- The operator must maintain sufficient L1 balance to prepay fees for each graph.
- Fee prepayment:
- ~10,000 sats per graph
- At startup, at least 50,000 sats must be deposited into the prepayment pool.
- If the prepayment pool is exhausted, the operator must top it up to at least 50,000 sats; otherwise, no new graphs will be generated.
- If no challenge occurs, most of the prepaid fees will be refunded.
- Fee costs:
take1: ~2,000 sats- If a graph is skipped (e.g., another operator initiates
take1/take2for the same instance): ~300 sats
Layer 2 (GOAT Network)
- The operator must stake PBTC on L2.
In theory, the staking token should not be PBTC; Currently PBTC is used on testnet for convenience.
Addresses
- Testnet Gateway:
0x440c6dCA87C3511E1eBf4FDB1f584ddaA49dD029(opens in a new tab) - Testnet StakeManagement Contract:
0x4B6BD356FE9Ad077c6E3691BB2838e814B3F4032(opens in a new tab) - Testnet PegBTC Contract:
0xdA97429ea2082334C63813f092B6A6209bfC4DEb(opens in a new tab)
Staking Process
- Call
stakeManagement.registerPubkey(xonly-pubkey) - Call
PegBTC.approve(stakeManagement_addr, amount) - Call
stakeManagement.stake(amount) - Call
stakeManagement.lockStake(amount)
Requirements
- A compressed public key is typically 33 bytes, starting with
02or03.
The x-only public key is the following 32 bytes (i.e., remove the leading02or03).
It is recommended that the node provides a method to derive the x-only public key fromBITVM_SECRET. lockStake_amount ≤ stake_amount ≤ approve_amountlockStake_amount ≥ 60000000000000000 (0.06 PBTC)
Eachdisproveslashes 0.03 PBTC.
Once the stake drops below 0.06 PBTC, no new graphs can be generated.
More details see our GOAT BitVM2 White Paper (opens in a new tab).
To become an operator or challenger, you need to run a BitVM2 Node.
Run BitVM2 Node
Installation
- Build from sourcecode
cargo install --git https://github.com/GOATNetwork/bitvm2-node bitvm2-noded- Download from Github releases
Download the binary from bitvm2-noded releases (opens in a new tab).
After the installation, run the bitvm2-noded --version to check that the version should be 0.1.0.
$ bitvm2-noded --version
bitvm2-noded 0.3.1Run a Node
You generate a file .env in your workspace, you can also download a .env template from here (opens in a new tab).
Specially, you need to prepare for your keys as below.
- PEER_KEY: Node peer key
$ bitvm2-noded key peer
PEER_KEY=
PEER_ID=- BITVM_SECRET: Your Hex-format private key, which is used to submit a challenge to the operator's reimbursement in BitVM2 graph.
After you set up the .env, you need to deposit some tBTC4 (Bitcoin Testnet4) to your P2WSH address:
$ bitvm2-noded key funding-address
Funding P2WSH address (for operator and challenger): tb1q…It prints a seed and a P2WSH funding address.
Run the node with run.sh (opens in a new tab)(This is a link to our github).